You may not know many people who have studied in Australia, but its 43 universities are in fact some of the most popular in the world for international students.
This shouldn’t come as a surprise, since Melbourne and Sydney are two of the best cities for students, and there are other idyllic locations with world-leading universities elsewhere on the island. The education system and application process is different from other Anglophone countries, so we’ve collected the information that you’ll need each step of the way.
Universities
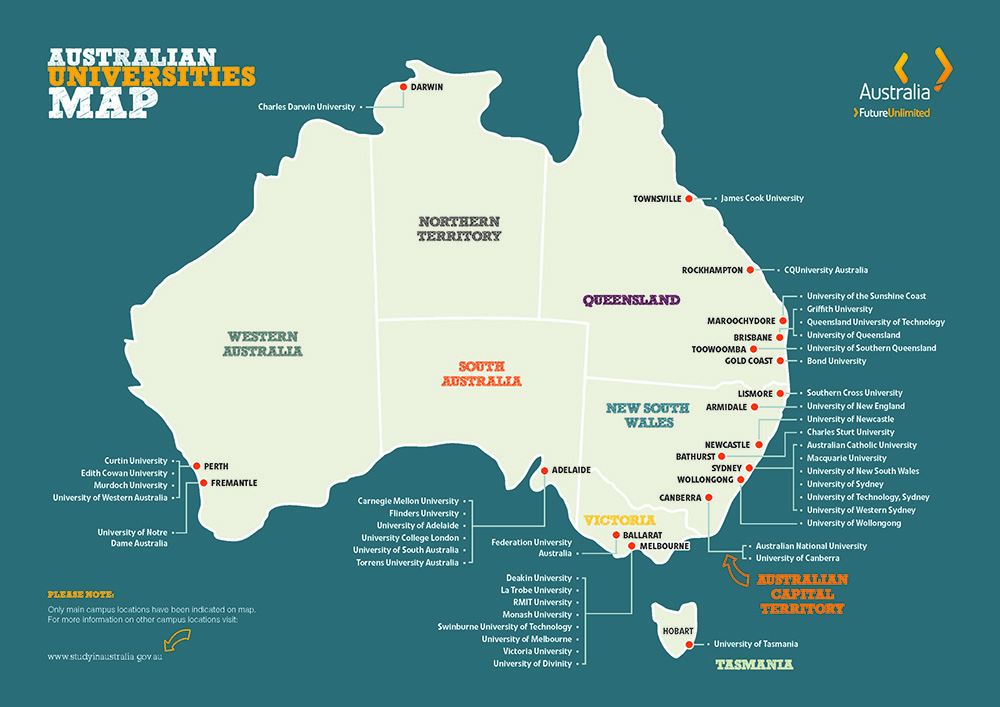
The universities are mostly clustered on the East Coast, with a total of 21 institutions in Brisbane, Sydney, Canberra and other towns in Queensland and New South Wales.
A further eight universities are based in Melbourne, another six in Adelaide on the Southern Coast, and one in between Adelaide and Melbourne.
On the other side of the island, there are five universities on the West Coast in Perth and Fremantle, and just one in Darwin, far to the north. The 43rd university is in Hobart on the island of Tasmania, and completes the country, with at least one university in each state or territory.
Explore Australia’s top universities
If you’re heading abroad for the academic experience, you’ll be interested to know that these institutions are some of the best in the world. Six universities in Australia are ranked in the top 100 in the THE World University Rankings. The top university in the country is the University of Melbourne.
Even the young institutions you may not have heard of are nonetheless reaching world-leading standards. More than a quarter of Australia’s universities in the top 100 universities under 50 years old. These up-and-coming institutions include the University of Technology, Sydney; Charles Darwin University and Queensland University of Technology.
It is very common in Australia for students to take double or combined degrees, choosing two subjects such as arts and science, arts and law, or commerce and engineering. Degrees typically take three years, but combined courses and some specific subjects can take longer.
If you want to quickly become more specialised than American universities allow for at an undergraduate level but still want the flexibility to study more than one subject, then Australia offers just that middle ground. In the first year you’ll be taking a range of options – about four subjects each semester.
The middle ground extends further. While courses are fairly similar to the UK system, Australian universities are known to be generally more informal than their British counterparts. Teaching is more relaxed and you
may have more contact with the teachers through weekly tutorials with 10 to 30 students.
Wherever you are in Australia, you’ll likely enjoy an outdoors way of life, with regular trips to the beach and national parks. Expect surfing, barbecues, hiking and biking to feature somewhere along the way.
The 10 most beautiful universities in Australia
Best universities in Australia
International perspective: a Zambian student in Australia
Trading America for Australia: my mother sent me to study 9,000 miles away!
The cost of studying at a university in Australia
9 things every international student should know about Australia
Studying overseas: guide to Australia, Canada, the UK and the USA
Admissions
Like Australian students, you have the option to start university in the first semester (March-June) or the second semester (July-October).
If you want to start in the first semester, your application must reach the university by December at the latest. Most domestic students will get their application in much earlier, and it is often a good idea to do so, since universities can return with a decision just weeks later.
The latest deadline to start in the second semester is in May, but again, it would be wise not to wait that late.
In addition to completing an application form online, by mail or in person, you will also have to pay a one-time application fee, and in most circumstances provide the results of an English as a second language test, such as Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) or International English Language Test System (IELTS).
You should send any test results directly to the institution when you receive them. Many Australian universities are represented by education agencies, so if you’d like to outsource some of the application process, it’s still best to do your own research and narrow down university options, and then check which agencies represent your top choices.
Funding
To study an undergraduate degree, you’re looking at tuition fees between A$15,000 (£8,400) and A$33,000 (£18,400) per year. But you won’t necessarily have to pay this all on your own. There are a number of Australian government scholarships and funding opportunities directly from the universities that can help you to meet the costs.
In particular, the Australia Awards scholarships are available only to international students from Asia, Africa, the Middle East and the Pacific. The closing dates for applications are mostly in April, but this differs for different countries.
A handy search tool for all scholarships available for international students who meet different criteria is managed by the Australian government on their website.
Visa
In almost all cases, you’ll need to apply for a student visa (subclass 500) for the duration of your full-time studies, except for research-driven postgraduate study.
You can only apply when you have accepted a place to study at a specific university in Australia, as you will need an offer letter or enrolment letter with your application. In addition to online or paper forms, you will also need to demonstrate that you have funding (personal or scholarship) for your stay, and you may need a health examination.
Just as with the university application, you must also provide an English as a second language test result, and your past academic record. You must also be covered by health insurance, which can be arranged using Overseas Student Health Cover.
The application can cost about A$550 as a one-time fee. Depending on the duration and start date of your studies, you will be able to stay one or two months in Australia after your degree ends. During your studies, you can leave and re-enter Australia multiple times.
If you want to work in Australia after graduating, you can apply for temporary visas, some of which are pathways to permanent residencies. Permanent visas are open to skilled workers only, and depend on qualification, work experience and sometimes employer sponsorship.
At first, the most common work visa for for graduates is the Temporary Graduate visa (subclass 485), which has two similar streams, differing only in the level of qualification that students must have received in Australia. Both options provide an extended visa for between 18 months and four years after graduating. More information can be found on the Department of Immigration and Border Protection website.