Growing numbers of sixth-formers in England are choosing all of their A levels from a single subject group, significantly limiting their degree choices and putting struggling university departments under greater strain, new research warns.
While 18 per cent of students in 2003-04 chose their AS and A levels from a single major grouping – science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM), social sciences, humanities or arts – by 2021-22 this had almost doubled to 35 per cent, according to a report published by the British Academy on 14 August.
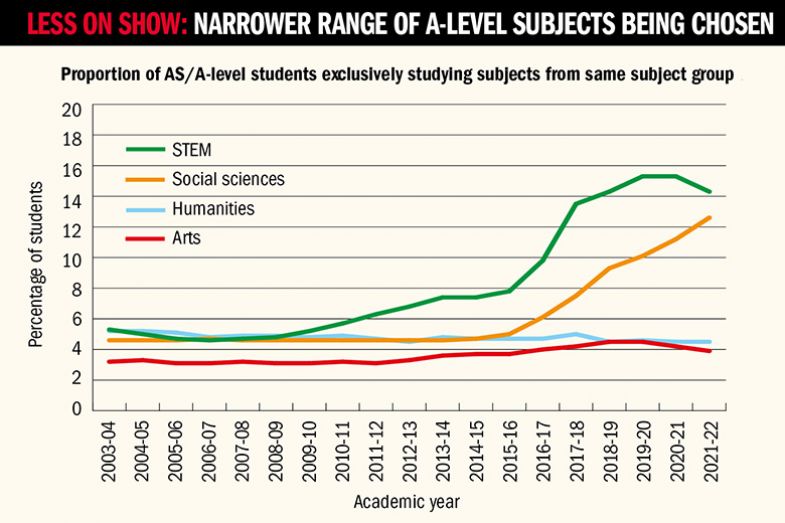
All but three percentage points of the rise post-dates 2015-16, when AS and A levels were “decoupled”, meaning that AS levels no longer contributed to A level results, and the average number of subjects studied dropped from five that year to three in 2019.
The arts and humanities have been squeezed the hardest. Between 2003-04 and 2015-16, the proportion of sixth-formers studying humanities subjects was stable at just below 60 per cent, but since then there has been a steady decline, with only 38 per cent taking humanities subjects in 2021-22.
The decline in arts subjects has been more gradual, with 24 per cent taking courses in this area in 2021-22, compared with 42 per cent in 2006-07.
In contrast, social sciences and STEM uptake has remained fairly stable at just over 60 per cent and in the region of 50 per cent respectively.
And more students are choosing only to take subjects from these areas: while the proportion of students taking only STEM courses grew gradually from 5 per cent in 2003-04 to 8 per cent in 2015-16, it accelerated to 15 per cent in 2019-20 and has stayed stable since then.
The proportion of students taking only social science subjects more than doubled from 5 per cent in 2015-16 to 13 per cent in 2021-22.
It is thought that 2011 Russell Group guidance advising school-leavers wishing to study at one of its member universities to take more traditional A levels and to avoid too many “soft” subjects, which was not revoked until 2019, might have affected student choices, while the increase in tuition fees in 2012 is thought to have incentivised students to prioritise STEM qualifications, which are often associated with higher earnings.
However, the consequence has been schools and colleges offering fewer courses in the arts and humanities, the academy warns. For example, while 78 per cent offered French in 2009-10, this fell to 54 per cent in 2021-22, while music went from 73 per cent in 2007-08 to 42 per cent in 2021-22.
Molly Morgan Jones, the academy’s director of policy, said the failure to address the decline of arts and humanities in post-16 education would have “knock-on effects, not only for these subjects in UK universities but also on the skills young people take out into the workforce and the wider world”.
“Higher education and research are under strain, and the humanities and arts are bearing the brunt of many departmental closures,” she said. “Breadth and balance should be at the heart of any future post-16 curriculum and should not be negatively impacted by any future reforms.
“The school curriculum should be interconnected and equitable, allowing and encouraging all students from all backgrounds to study a range of disciplines. Our students’ skills, and our societal growth, depend on it.”
后记
Print headline: Diversity of subjects narrows for A levels




