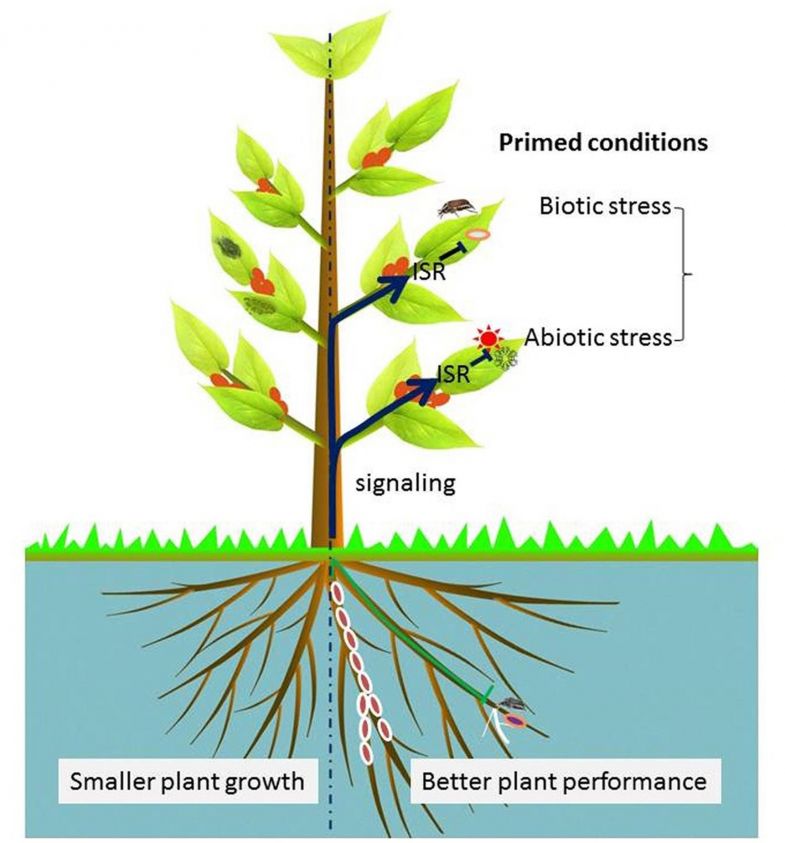
- What Is There in Seeds? Vertically Transmitted Endophytic Resources for Sustainable Improvement in Plant Growth
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00024
Endophytic microbes, or the bacteria and fungi that live within plants, are beneficial to their development. In particular, endophytic microbes found inside seeds help improve the biomass of plants and their yield under stressful environments. However, their potential remains underexplored. Scientists from Korea and Oman now provide a review focusing on these endophytes and their role in the production of metabolites and enhancing plant growth and crop efficiency.
- Daily water level forecasting using wavelet decomposition and artificial intelligence techniques
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.050
Reservoirs play an important role in water supply, flood mitigation, and hydropower generation. For efficient reservoir operation, accurate forecasting of water level for reservoir inflow is critical. An international research team now develops and applies two hybrid models for water level forecasting based on wavelet decomposition using artificial neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system.

- Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2013.01.007
Irisin, a recently discovered hormone, is known to play a role in the brown-fat-like development of white fat and heat production. In a new study, Kyungpook National University scientists show that irisin levels are decreased in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared to those with normal glucose tolerance, suggesting that irisin may be factor in glucose intolerance and T2D.

- Nitric oxide regulates plant responses to drought, salinity, and heavy metal stress
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.02.003
When exposed to stressful environments, such as drought, heat, and high-metal concentrations, plants release signalling molecules that help them adapt to the stress. Nitric oxide (NO) is one such signalling molecule whose exact role in plants is unclear. An international research team now reviews and discusses the effect of external application of NO to plants under abiotic stresses, showing that NO mitigates negative effects of stress and enhances antioxidant activity in most plant species.
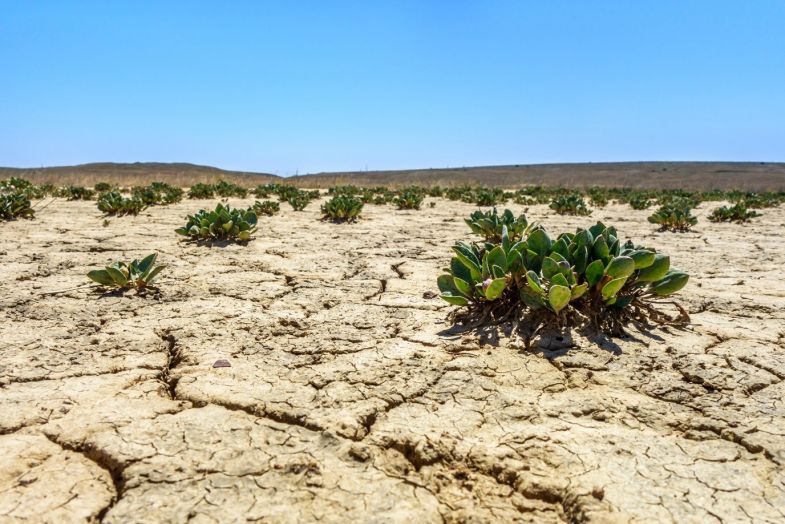

- Inoculation of abscisic acid-producing endophytic bacteria enhances salinity stress tolerance in Oryza sativa
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.01.010
Plants exposed to high-salinity environments suffer from impeded growth and reduced crop yield. While symbiotic plant bacteria can help counter stress and enhance tolerance, their ability to produce abscisic acid (ABA), a hormone important for plant development, is unclear. Now, an international research team has shown that the bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RWL-1 increases the tolerance of the rice crop plant, Oryza sativa, under salinity stress through the production of ABA.

- A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.015
Nanomaterials attract much attention due to their diverse applications. As a result, nanomaterial manufacturing techniques, such as electrospinning, have become popular owing to their ability to fabricate nanostructures with desirable properties. Researchers from Korea and Saudi Arabia now provide an overview of the electrospinning parameters and other factors influencing the fabrication of nanofibers and their application in tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensing.

- Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Neutrophils in Tumor Microenvironment
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6058147
The activation of immune cells, such as neutrophils, are known to favour the growth of cancerous tumors and metastasis. Moreover, neutrophils often recruit macrophages in inflammatory environments that, in turn, affect neutrophil function. Now, a review by scientists from Korea examine the various possible interactions between tumor-assisted neutrophils and tumor-assisted macrophages in tumor microenvironments.
- Targeting Glutamine Metabolism for Cancer Treatment
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2017.178
Cancer cells require energy to proliferate and, therefore, need to adapt their nutrient metabolism to meet the high energy demand. Glutamine, an amino acid abundant in plasma, often provides nutrient to cancer cells and help them survive during metabolic stress. A review by Kyungpook National University scientists now highlights the role and underlying mechanism of glutamine metabolism in cancer cell growth and discusses its potential as a therapeutic target in treating cancer.

- Two-dimensional (2D) Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets with superior adsorption behavior for phosphate and nitrate ions from the aqueous environment
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.183
With the development of modern industries and rapid urbanization, eutrophication, or the increase in phosphorus and nitrogen in aquatic ecosystems, has come to pose a serious issue in water usage. Addressing this issue, scientists from India and Korea demonstrate adsorptive removal of nitrate and phosphate ions from water bodies using two-dimensional MXene nanosheets, highlighting its potential for efficiently removing toxic water pollutants.

- Urban planning and building smart cities based on the Internet of Things using Big Data analytics
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2015.12.023
With the rise in population in urban cities, there is a subsequent need for quality services and infrastructure. The increasing need for smart devices, in particular, is giving way to a new era of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. In light of this, researchers from Korea propose a combined IoT-based system for developing smart cities and a Big Data analytics-based approach to urban planning.

- Improvement in phytoremediation potential of Solanum nigrum under cadmium contamination through endophytic-assisted Serratia RSC-14 inoculation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4647-8
Hyperaccumulator plants, which accumulate particular metals in their tissues at higher concentrations than normal plants, offer suffer from the presence of toxic metals such as cadmium (Cd). Endophytic bacteria, symbiont microbes found in plants, can, however, come to the rescue. Now, an international research team demonstrates that an endophytic bacteria Serratia sp. RSC-14 isolated from the hyperaccumulator plant Solanum nigrum could relieve the toxic effects of high Cd concentration.

- Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-13
Tolerance of crop plants against abiotic stresses, such as heavy metal concentrations in soil, can be enhanced by applying silicon. However, the mechanism underlying silicon’s protective action is not understood. In a new study, scientists examine the role of silicon in mitigating the toxic effects of cadmium and copper in the rice crop plant, Oryza sativa, unravelling new insights.

- Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2014.894587
An international research team examined the role of rhizobacteria strains, endophytic bacteria that promote plant growth, in mitigating salinity and drought stress in the cucumber plant, Cucumis sativas, demonstrating higher biomass and chlorophyll content in plants treated with rhizobacteria strains compared to non-treated plants.

- Melatonin: Awakening the Defense Mechanisms during Plant Oxidative Stress
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040407
When exposed to extreme environmental conditions characterized by drought, acid rain, high salinity, and heavy metal toxicity, plants show several physico-chemical responses triggered by the molecule melatonin, which plays the role of antioxidants in plants. In a new study, researchers show that applying melatonin to crop plants even externally can improve their growth and tolerance against stressful environments through regulation of their antioxidant systems.

- The Effect of Experience Quality on Perceived Value, Satisfaction, Image and Behavioral Intention of Water Park Patrons: New versus Repeat Visitors
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.1968
Researchers from Korea and USA put forth, in a new study, a conceptual model for exploring how perceived quality of experiences affect perceived value, image, satisfaction, and behavioural intentions of first-time and repeat customers and patrons of water parks.